Table of Contents
Have you measured high BMI, even though you regularly train and eat healthy? Where did the mistake happen? In this article, we will explain when high BMI does not mean obesity and why bodybuilders should not rely on it.
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It is a method of determining the health risk of obesity based on a person’s body weight and height. BMI is indicated in the form of a number that will rank you in the BMI category based on your weight status. [1]
BMI calculation is a form of indirect fat measurement. However, experts have found it to be a relatively reliable indicator for most people. Indeed, research of BMI calculations has yielded comparable compliance with more complicated body fat measurements such as weighing under water. [2]

How to calculate BMI?
BMI can be calculated very easily and quickly. All you need is your measures and a calculator. Then you just need to follow the formula below. [2]
BMI = your body weight in kg / (height in m)2
For example, if you have a weight of 68 kg and a height of 165 cm (and therefore 1.65 m), you can calculate the BMI as follows:
- BMI = 68 kg / (1,65 m)2
- BMI = 24,98
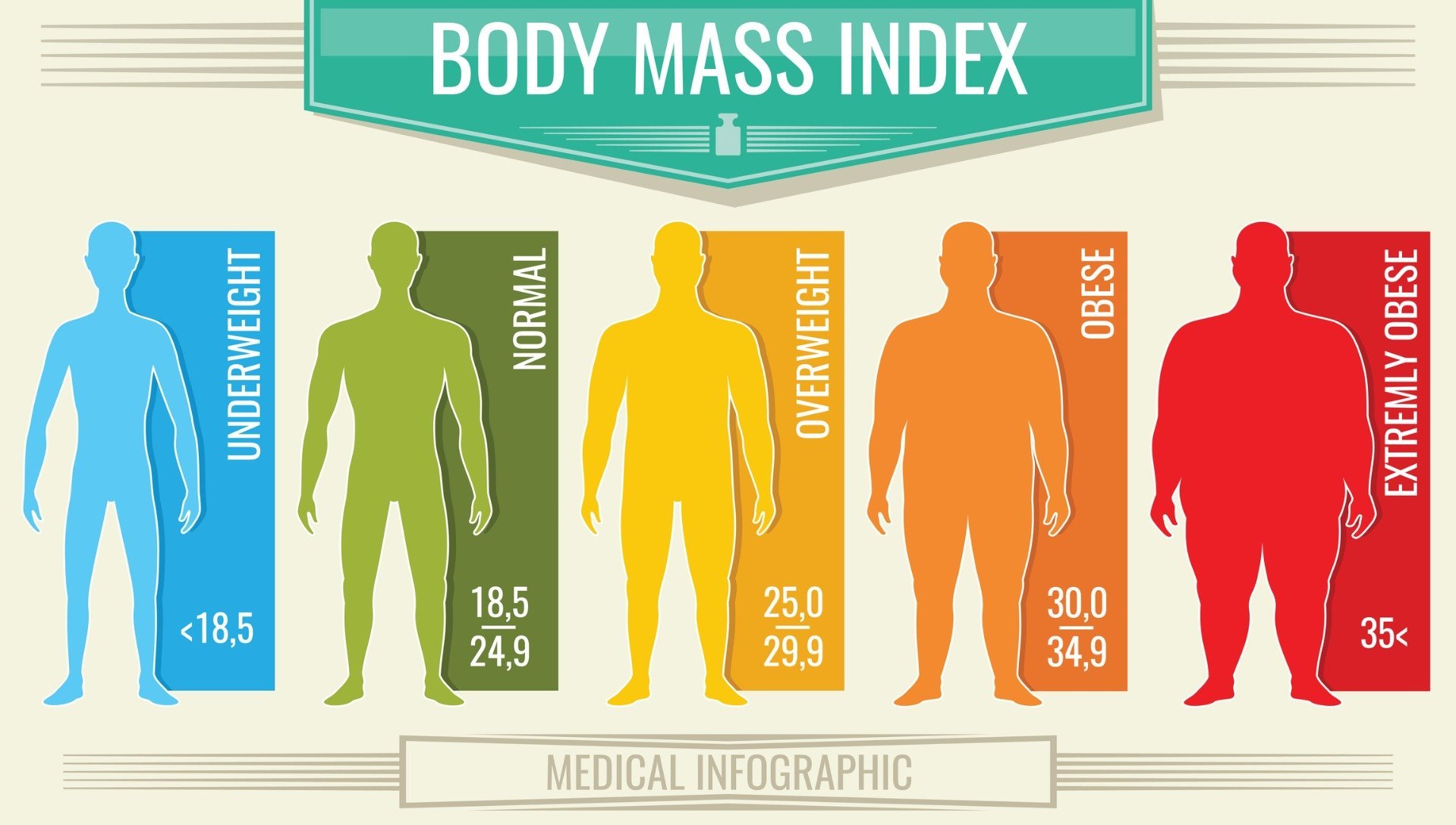
What does the resulting BMI value mean?
The result of BMI is a number that determines your weight status and possible health risk. The following table shows standard categories according to BMI ranges for adults. Compare your BMI result with the numbers in this table to see what your body composition is. [3]
| below 18,5 | underweight | medium |
| 18,5 – 24,9 | healthy weight | low |
| 25,0 – 29,9 | overweight | medium |
| 30,0 and more | obesity | high |
But what does that mean? Individual BMI categories can be interpreted as follows. [9]
- BMI below 18.5 indicates that you are underweight. This means that you should see your doctor for advice on gaining weight in a healthy way.
- BMI of 18,5 to 24,9 indicates that you have a healthy weight for your height. Given this positive outcome, you have less predisposition to serious health problems.
- BMI of 25,0 to 29,9 can be interpreted as slightly overweight. You should therefore consider weight loss by acquiring healthy habits such as balanced eating and physical activity. You can be inspired by our fitness recipes and training plans.
- BMI of over 30 draws attention to the developed overweight to obesity, which may endanger your health. You should therefore consult your doctor for options for reducing weight and body fat.
The following table from the World Health Organization provides an even more specific definition of BMI values. [9]
| Underweight | <18,50 |
| Severe malnutrition | |
| Medium malnutrition | 16,00 – 16,99 |
| Mild malnutrition | 17,00 – 18,49 |
| Healthy weight | 18,50 – 24,99 |
| Overweight | ≥25.00 |
| Mild obesity | 25,00 – 29,99 |
| Obesity | ≥30.00 |
| Obesity type I | 30,00 – 34,99 |
| Obesity type II | 35,00 – 39,99 |
| Obesity type III | ≥40.00 |
You might be interested in these products:
What are the health risks of high and low BMI?
While a healthy weight is a prevention against diseases and cardiovascular problems, obesity carries considerable health risks. People with a BMI over 30 are more likely to experience difficulties like [2]:
- hypertension
- type 2 diabetes
- coronary heart disease
- stroke
- arthritis
- some types of cancer
- respiratory problems
Even a low BMI does not guarantee good health. People with a BMI below 18.5 are at risk of malnutrition, osteoporosis, anemia and a variety of problems that may result from nutrient deficiency. Low BMI may also be a signal of hormonal, digestive or other problems. [2]

Who is BMI useful for?
Of course, BMI results are not 100% accurate. However, for a large proportion of the population, BMI serves as a practical tool to identify overweight or obesity. These data will help your doctor determine the increased risk of heart disease. In addition to BMI, blood cholesterol and blood sugar as well as blood pressure are decisive factors. [6]
For adolescents and children, BMI is calculated in the same way, but the results are interpreted in a different way, with respect to age and gender. For example, young adolescent girls automatically have a higher percentage of fat than their male peers. [6]
The difference between BMI and RFM
The disadvantage of BMI is that it focuses on numerical values such as total body weight in relation to height and does not take into account the amount of body fat. It is the percentage of fat that speaks of a person’s health more than his or her weight. The body weight in kilograms does not distinguish the amount of fat compared to muscle mass, bones, organs and fluids in the body. [6]
This is the fundamental difference between BMI and RFM. RFM is another possibility of indirect calculation of body fat. This is the way established by The Cedar Sinai. Its researchers have processed more than 300 possible body fat patterns on a sample of 3,500 patients and compared them with the results of the DXA scan, which is currently the standard technology for body composition analysis. [7]
The winning formula corresponds to a relative fat mass (RFM). Like BMI, you can calculate it in the comfort of your home. You only need a meter. How to do it? [7] First, measure your height in centimetres. Then measure the waist circumference. Enter the resulting values in the equation below based on your gender. [7]
- Man: 64 – (20 x height/waist circumference) = RFM
- Woman: 76 – (20 x height/waist circumference) = RFM
For example, if you are a man with a height of 180 cm and you have a waist circumference of 80 cm, your formula will look like this:
- 64 – (20 x 180/80) = RFM
- 19 % = RFM
Based on RFM, you can estimate what your fat percentage is. However, if we look at the above figures, we find that a bodybuilder with a lower body fat percentage could have a weight of 180 cm and a weight of 80 kg. How is it possible? [7]

Deficiencies of BMI and RFM
Both BMI and RFM have certain limits. While they can almost accurately determine the health risk and fat levels for the majority of the population, there are some limitations that BMI and RFM calculations do not take into account at all. These are differences based on the sex, age and sporting activity of individuals. They are specific as [2] [4] [5]:
- Amount of muscle mass – most athletes have low fat but higher weight of muscle tissues. This is automatically reflected in body weight and therefore higher BMI.
- Level of activity – BMI can also be misleading if a person has little muscle while having a higher body fat ratio. This is the case for older people who are not active and therefore do not have enough muscle mass.
- Body shape – your body type can tell you where your body fat is stored. Individual types of female characters include a rectangular figure, a pear shape, an apple shape, an inverted triangle, and an hourglass. If you have a character like an apple and therefore fat is stored mainly in the abdomen, you are more likely to have health problems. A waist circumference of over 100 cm for men and 89 cm for women may indicate that you have too much visceral intra-abdominal fat. This type of fat surrounds the internal organs, increasing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders or diabetes. [6]
- Age and gender – the body composition changes with age. There have been differences since puberty, when male and female hormones change body shape. After entering menopause, the hormone balance is re-established and the way women store fat changes.
This suggests that BMI is a useful tool for rapidly assessing physical disposition for the general population rather than for bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts. Therefore, athletes cannot consider BMI as reliable and decisive information. [5]

Methods of measuring fat for athletes
So how do you find out your body fat percentage if you are an athlete or bodybuilder? You can use methods that obtain results from the analysis of the overall body composition. The most common fat calculation techniques include skin thickness measurement, hydrodensitometry or bioelectric impedance.
- Hydrodensitometry is a complex weighing of a person below the water level. This is a very complicated process that requires special environments and tools, so most experts use simple caliper measurements of skin thickness.
- Caliper – is the best-known method of measuring body fat. It works by measuring the thickness of the skin on different parts of the body and then putting the values into the formula. The result is finding out how much fat you have in your body.
- Bioelectric impedance – is a common method for determining body fat percentage. It is a measure of body composition based on the speed at which electric current passes through the body. Adipose tissue causes more resistance (impedance) than muscle mass and slows down the speed at which the current moves. This method determines the total body weight, percentage and amount of body fat, muscle mass, water and even bone tissue. Its values may be slightly influenced by the level of hydration and other factors, but it nevertheless provides relatively accurate results. Body fat scales can be found in specialist stores and are also available for home use. [2] [8]

However, even these methods will not guarantee that your results will be completely accurate. However, if you decide to have your fat measured by a specialist, make sure that you are always measured by the same person (if caliper is used for measurement), while using the same devices.
You should also remember that large fluctuations in body fat are not beneficial to your health. Therefore, be careful at the time of losing fat before the competition compared to the percentage of fat in the off-season. [6]
What method do you try to measure body fat? Do you rely on the BMI result or do you prefer other forms of calculation? Write us your feedback in the comments and show off your photos before the contest. And if this article has brought you new information, support it by sharing.
[1] Katherine Marengo - BMI calculators and charts – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323586.php
[2] Elizabeth Quinn - WHat the body mass index BMI measures? – https://www.verywellfit.com/bmi-what-is-bmi-or-body-mass-index-3120088
[3] A large selection of easy to use fitness calculators! – https://www.bodybuilding.com/content/a-large-selection-of-easy-to-use-fitness-calculators.html
[4] Wendy Bumgardner - Ideal weight by height calculator chart – https://www.verywellfit.com/ideal-weight-calculator-chart-3878254
[5] How much is BMI accurate for bodybuilders? – https://www.myfitfuel.in/mffblog/much-bmi-accurate-bodybuilders/
[6] Andrea Cespedes - How to calculate BMI for a bodybuilder – https://www.livestrong.com/article/421339-bmi-calculator-for-bodybuilders/
[7] TC Luoma - Tip: A better way to calculate body fat percentage – https://www.t-nation.com/training/tip-a-better-way-to-calculate-body-fat-percentage
[8] Malia Frey - Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) - Use a BIA scale to meet fitness and weight loss goals – https://www.verywellfit.com/bioelectrical-impedance-analysis-bia-3495551
[9] World Health Organization - BMI classification – http://www.assessmentpsychology.com/icbmi.htm
[10] Yvette Brazier - Measuring BMI for adults, children, and teens – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323622.php


Add a comment